On the one hand, banking solutions offer flexibility and a management approach geared investment. On the other hand, insurance companies add a protection in the event of death or disability.
What is the 3rd pillar?
The 3rd pillar is an integral part of the Swiss pension system, alongside the AHV (1st pillar) and the occupational pension scheme (2nd pillar). It is a voluntary savings scheme designed to improve living standards in retirement, while offering attractive tax benefits. There are two types: Pillar 3a, known as "linked", and Pillar 3b, known as "free".
The 3a is reserved for people with a income subject to AHV It allows you to build up long-term savings, with objectives such as supplementing your retirement, optimizing your tax situation, and protecting your loved ones in the event of an unexpected event.
Characteristics of Pillar 3a banking
Opting for a banking solution for your 3rd pillar A in Switzerland is a popular choice for many savers seeking greater flexibility and investment opportunities.
Flexible payments
Deposits are free, so you can adjust your contributions according to your budget and needs. You can stop or resume payments at any time.
Limits and drawbacks
Unlike insurance solutions, a bank 3rd pillar does not offer no cover in the event of death or disability, and returns are highly dependent on the financial markets for investment solutions, which can lead to losses in times of crisis.
100% savings contributions
The entire amount paid in is allocated to savings, without any risk coverage. This makes it a particularly suitable solution for young professionals with no family responsibilities, who prefer freedom and low management fees.
Advantages of 3a banking
- Flexibility: you decide what you want to pay in at any time
- 100% savings: what you pay in goes directly to savings
- Reduced costs: management fees are lower and you pay no risk coverage
Pillar 3a insurance features
Choosing an insurance solution for your 3rd pillar in Switzerland is a popular option for those wishing to combine savings and protection. This type of provident scheme offers additional guarantees in the event of death or disability, while building up capital for retirement.
Savings and protection combined
In the event of death, the capital sum is paid directly to the designated beneficiaries. In the event of disability, the insurance generally covers the premiums, enabling savings to be maintained until the scheduled maturity date.
Long-term commitment
Premiums must be paid regularly, according to the amount set out in the contract. This helps discipline savings, but can be a constraint for those with fluctuating incomes.
Guaranteed returns
Insurance solutions often offer a guaranteed minimum return, which reduces the risk of capital loss. Some formulas include surplus dividends, allowing you to benefit from an additional return.
Profit sharing
As part of a 3rd pillar insurance plan, the policyholder can benefit from a profit sharing. This means that if the insurer achieves best-in-class performance As a result, a portion of these profits is passed on to customers in the form of additional returns. This participation may not be guaranteed, but it does improve overall returns over the long term.
Waiver of premiums in the event of disability
Another advantage of an insured 3rd pillar is the waiver of premiums in the event of disability. In practical terms, if the insured becomes unable to work for medical reasons, the insurance takes over and continues to pay into the policy on his or her behalf. Savings therefore continue as normal, without the insured having to pay new premiums, guaranteeing that the capital will be built up even in the event of a serious setback.
Higher costs
3a insurance solutions generally include higher costs than bank products. These costs cover several aspects management fees of the contract, the board proposed by the insurer or intermediary, as well as the risk premium related to death and disability coverage. These costs reduce the net return, and can be explained by the security and protection benefits, as well as by the more expensive nature of the benefits. complex such a contract.
Advantages of 3a insurance
- Extra blanket: the insurance pays benefits in the event of death or disability
- Profit sharing: part of the insurer's profits are redistributed to the policyholder
- 2-in-1 model: 3a endowment life insurance offers combined death/disability and savings protection
- Guaranteed return: a minimum amount of capital can be guaranteed, regardless of the health of the financial markets.
- Waiver of premiums in the event of disability: in the event of a GI, the insurer saves on your behalf.
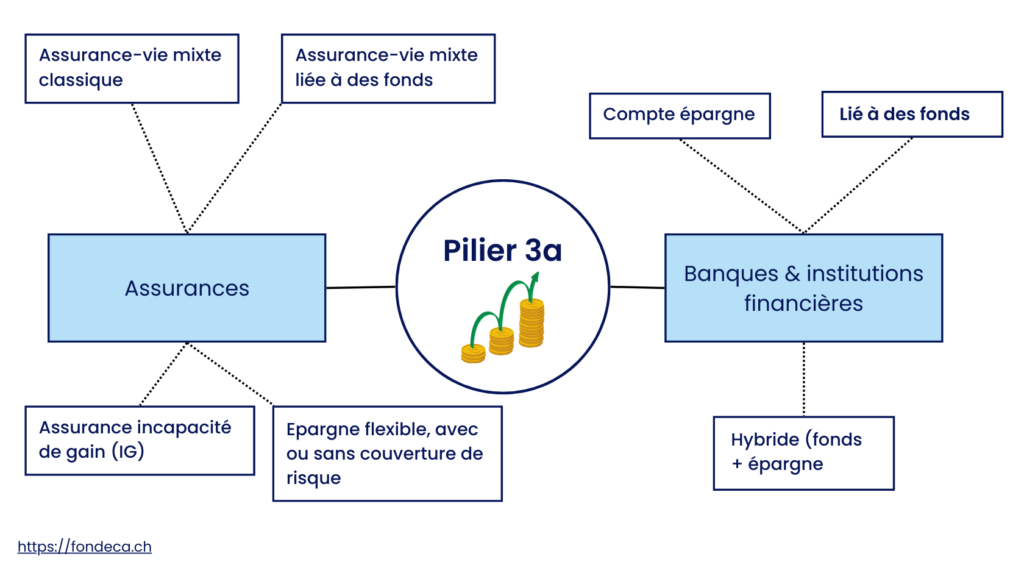
What types of 3rd Pillar A are offered by banks?
In Switzerland, when considering opening a 3rd pillar A account with a bank, there are two main options: the classic 3a savings account and investment in 3a pension funds.
3a savings account
The 3a savings account is the simplest and most traditional form of Pillar 3a banking. Here, savings are deposited in a blocked account, earning a fixed interest rate set by the bank. This rate, while currently modest (below 1.1 %), has the advantage of offering a high level of capital security.
This solution is ideal if you plan to withdraw your 3a (for example, for a property purchase) in the 5 years in the future. However, you should be aware that, over the long term, the return offered by this type of account is generally lower inflation. So, for young working people or those with several decades ahead of them, this option may well prove to be the right one. low-performance in terms of capital formation.
Pillar 3a banking in funds
In addition to the classic savings account, many banks now offer 3a provident funds. It's no longer just a question of saving, but of investing your 3a assets in the financial markets, through funds diversified (ETFs, equities, bonds, real estate, etc.).
Several strategies are possible, depending on the investor profile (cautious, balanced, offensive), influencing the equity component. But unlike the savings account, the capital is not not guaranteed in a 3a fund: the value of your savings may therefore fluctuate, depending in particular on the performance of the financial markets. Nevertheless, on the long termstudies show that equity investments have historically offered better returns than fixed-rate products.
What types of 3rd Pillar A are offered by insurance companies?
Insurance companies offer a more flexible 3a in terms of savings and risk coverage. They do, however, charge higher fees.
Classic combined life insurance
The traditional form of 3rd pillar A insurance is thelife insurance classic mixed. In this model, the premiums paid by the policyholder are used both to build up a interest-bearing savings at a guaranteed interest rate and to finance coverage in the event of death or disability.
In practical terms, this means that at the end of the contract (for example, at age 64 or 65), the policyholder receives a capital sum made up of his or her payments, guaranteed interest and, if applicable, an additional premium. profit sharing if the company performs better than expected. In the event of premature death or disability, an insured sum is paid to the beneficiaries or to the policyholder.
This type of contract is ideal for savers who value capital security and want to combine retirement savings with family protection without exposure to financial market risks. However, returns are lowand performance is often lower than that of a 3a bank account because of the additional risk-related costs.
Endowment life insurance
For those wishing to benefit from higher potential returns, insurance companies also offer unit-linked life insurance. Here, the savings portion is not placed in a guaranteed-rate account, but invested in the financial markets via in-house, bank or ETF funds.
A risk hedging (death and often disability) is maintained throughout the term of the contract, and savings grow in line with fund performance. If markets are favorable, savings can grow faster than on a conventional savings account. On the other hand, the cash surrender value of the contract may fluctuate downwards in the event of poor stock market results.
3a flexible
Finally, a growing number of insurers are now offering so-called 3a flexible. In these contracts, the emphasis is on a high degree of personalization: savings are invested in investment funds, but the policyholder can choose to add protection modules.
Possible options include :
- A death cover (fixed capital or proportional to savings)
- A disability insurance (with premium waiver or annuity payment)
- A disability insurance (payment of a lump sum or an additional annuity).
- Waiver of premiums in the event of disability (the insurance covers you in the event of disability)
The main advantage of these flexible solutions is that they enable you to tailor your pension plan precisely to your needs, whether in terms of savings, risks covered or degree of exposure to the markets. They also offer the possibility of modifying certain parameters (including premiums) during the term of the contract.
Comparison of banking VS insurance fees
When choosing between a Pillar 3a with a bank and a Pillar 3a with an insurance company, the question of costs is often at the forefront. At first glance, bank solutions seem more economical. However, a detailed analysis shows that the reality is more nuanced.
In banking, fees are mainly concentrated on the investment. They take the form of fund management fees (called TERfor Total Expense Ratio), which generally vary between 0.20 % (online service providers) and 1.50 % per annum. The more passive the solution (index ETFs, for example), the lower the TER. There is no death or disability protection: the bank offers only an investment vehicle.
In insurance, the situation is different. The funds chosen often have lower TERs - around 0.20 % to 0.45 % - because insurers prefer institutional funds with lower fees. In addition to these fund charges, however, there is the so-called contract performance reduction: this includes the insurance management fees as well as administrative costs. This reduction varies from one provider to another, typically between 0.5 % and 2.10 % per year.
This mechanism makes sense: in insurance, the 3a contract is not limited to a single product. investment. It also guarantees a death benefit, protects savings in the event of an unexpected event, and often offers options such as phased withdrawal before retirement. These services have a cost, but they meet a need for security that the banking solution does not.
Example of a banking VS insurance scenario
To illustrate the difference between a banking solution and a Pillar 3a insurance solution, let's take a simple example.
One person saves 600 francs per month for 35 years old. Gross market yield is estimated at 6.5% per year. In one case, savings are invested in bankwith no special protection. In the other case, it is invested in ainsurancewith a guaranteed death benefit and protection in the event of disability.
1. Bank development
- Parameter
- Value
- TER funds
0.41%
- External management fees
- Estimated net yield
- Estimated final capital after 35 years
CHF 714,900
- No death benefit
If the person dies after 1 year, the estate only receives accumulated savings (~7,250 CHF)invested in the stock market.
2. Insurance developments
- Parameter
- Value
- TER funds
0.25%
- External management fees
1%
- Estimated net yield
5,25%/year
- Estimated final capital after 35 years
CHF 635,000
- Immediate death protection
If the person dies after 1 year :
- It paid out only CHF 7,250
- His heirs receive CHF 200,000 guaranteed by the insurance.
Should I take out a 3a bank or insurance policy?
There is no universal answer to this question. The bank maximizes long-term performance by limiting costs, but offers no immediate protection against unforeseen events. Insurance, in return for a slight reduction in net yield, guarantees a higher death benefit from day one, protecting your savings against the vagaries of life.
The best choice depends on profile the saver: age, family responsibilities, savings capacity, risk appetite and personal priorities. A young single person with no financial commitments may prefer a pure banking strategy. A person wishing to secure a life project, protect their family or cover the risk of incapacity will find a more comprehensive and tailored solution in an insurance policy.
The key is to make a well-informed choice, understanding what each option brings, while keeping an eye on the bigger picture. transparent on the fees generated.
3A comparison chart in banking VS insurance
- Criteria
- 3A insurance
- 3A bank
- Payment frequency
Flexible
Determined in advance
- Type of investment
- Classic (simple savings)
- Mixed (savings/risk)
- 100% fund
- Classic (simple savings)
- 100% fund
- Surplus earnings
Profit sharing
No profit sharing
- Possible coverage
- Death cases
- Disability cases
No
- Bankruptcy guarantee
Amount guaranteed to 100%
Guaranteed amount up to CHF 100,000
- Waiver of premiums in the event of disability
Possible
No
- Investment horizon
Medium to long-term
Long-term
- Key benefits
- Risk insurance coverage
- Profit sharing
- Amount guarantee
- Higher surrender value
- Best financial performance after expenses
- Flexible payments
Frequently asked questions
No, not necessarily.
3a insurance modern often use index funds or ETFs with very low fees (TER from 0.20% to 0.45%), comparable to those of the best banking solutions.
Net performance depends above all on the contract chosen, the investment profile and overall costs (including yield reduction).
Because it offers a little more than just performance :
A death benefit guaranteed from the first payment,
Waiver of premiums in the event of disability,
Secure management at the end of the contract to protect accumulated capital.
For many people, this global security more than justifies a slight reduction in yield.
Yes, that's right.
It is possible - and in some cases advisable - to have several 3a contracts:
A banking contract in funds to maximize long-term returns,
A insurance contract to secure part of your capital and protect your loved ones.
This approach allows you to benefit from the advantages of each solution.
The insurance company immediately pays guaranteed death benefit often between CHF 100,000 and 250,000.
For example, even after just CHF 7,200 your heirs can receive CHF 200,000 (depending on the contract). In the bank, only savings actually accumulated are paid out (e.g. CHF 7,200 + any performance).
Yes, a 3a bank is generally more complement:
You can pay in what you want, when you want (within the legal limit).
You can stop payments without penalty.
With 3a insurance, you commit yourself to paying a regular premium over a fixed period. However, today's modern insurances offer greater flexibility (premium adjustment, release of the insurance in case of need).
Yes, but with caution. Cancelling a 3a policy in the first few years can lead to serious losses (cash surrender value less than premiums paid). That's why it's essential to choose a contract that meets your long-term needs before committing yourself.
The 3a bank account is more suitable for long-term savings, as you can choose not to pay into it for as long as you wish (no payment obligation).
Whether in banking or insurance, the maximum amounts are as follows:
- CHF 7,258 per year if you are an employee with a pension fund
- Up to CHF 36,288 per year (or 20% of net income) if you are self-employed (or employed) without a pension fund.