What is early retirement?
Early retirement is the decision to stop working before the legal retirement age. In Switzerland, the legal retirement age is 65 for men and 64 for women (soon to be 65).
Early retirement is treated differently depending on theOASI, BVG and tied personal pension plans.
At what age can I take early retirement?
- According to AVS (1st pillar): 2 years before normal retirement age (63 for men and 62 for women)
- According to LPP (2nd pillar): Most pension funds allow you to draw a pension from the age of 58.
- According to the tied individual pension plan (3rd pillar): 5 years before normal retirement age
Harmonization of retirement ages
The AVS 21 reform sets the reference retirement age at 65 for everyone. For women in the transitional generation (born between 1961 and 1969) who do not opt for early retirement, a lifetime pension supplement is planned.
1. Early receipt of AHV pension
The AVS pension covers basic needs. It is defined in stages, based on the average annual income (average AVS income earned during a person's lifetime, taking into account any gaps in contributions). The average income is capped at CHF 90,720 /year. You can find out your future AHV pension by consulting thescale 44.
Once your AHV/AVS pension has been defined, you will have to reduce it in line with the anticipated early retirement date (maximum 2 years before the reference retirement age):
- Anticipation period
- Reduction
- 6 months
- 1 year
- 1 year and 6 months
- 2 years
- - 3.4%
- - 6.8%
- - 10.2 %
- - 13.6 %
Early pension calculation
You can request an estimate of your AHV pension.
Example of early receipt of AHV pension
Let's imagine that Mr. Y decides to take early retirement 2 years before the reference age, and has an average annual income of CHF 85'000.
- He would normally receive a pension of CHF 2,460 / month or CHF 29,520 / year.
- As a result of the anticipation, he would only receive CHF 25,505 / year, or CHF 2,125.44 / month, for the rest of his life.
- 29,520 x (100% - 13.6%) = 25,505.28
AHV 2025 figures
- The maximum AHV pension is CHF 2,520 / month
- The minimum AHV pension is CHF 1,260 / months
- The maximum determining average annual income is CHF 90,720
2. Early receipt of BVG pension
Life LOB does not formally provide for the right to early retirement; however, most pension funds offer this possibility in their regulations. The minimum age for early retirement is set at 58 years old.
If you opt for early retirement, your retirement pension will be reduced by the following amount final according to a lower conversion rate0.15 to 0.25% per year of anticipation). Each pension fund has its own rules on this matter.
What are the BVG/LPP benefits for early retirement?
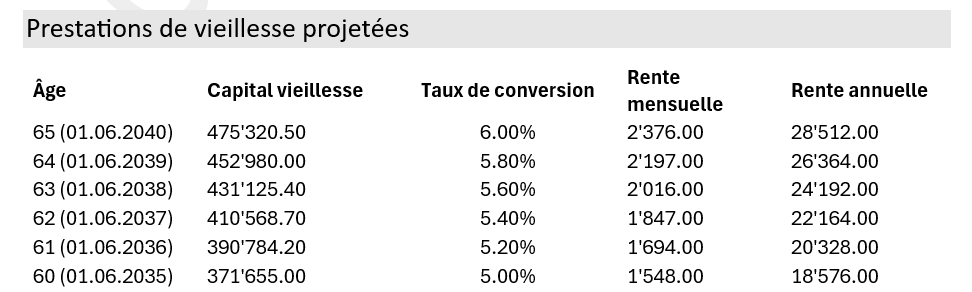
On your pension certificate, you can find details of your projected retirement benefits, based on your planned retirement age, with the conversion rate corresponding.
In the event of permanent departure abroad, outside the EU/EFTA, the capital can be withdrawn in full.
3. Early withdrawal of 3rd pillar A
Linked pension plan figures
In 2025, the following amounts can be paid into the tied personal pension plan:
- Employee affiliated to a pension fund: Up to CHF 7,258 / year
- Self-employed or employee not affiliated to a pension fund: 20% of income, maximum CHF 36,288
How do you fill the gaps when you retire?
It's essential to define your financial needs once you retire, and compare them with what you'll actually receive. If the gap is significant, several strategies are possible.
1. Buying into the pension fund
If you notice a discrepancy on your pension certificate redemption potential (linked to incomplete years or periods without contributions), you can pay an amount of unique or staggered to make up the shortfall. Every franc purchased is immediately deductible from your taxable income, and permanently increases your retirement assets and risk benefits (and therefore your future pension).
Note that after any redemption, a lock-in period of 3 years applies before any capital withdrawal.
2. Pillar 3a redemption (from 2026)
Starting in 2026 (for the 2025 tax year), it will be possible to retroactively buy back up to ten years of missed contributions to pillar 3a, at a rate of CHF 7,258 per year in addition to the regular contribution.
To be eligible for this purchase, you must have received income subject to AHV during the year in question, and have already paid the maximum contribution at the time of purchase. The amounts bought back are fully deductible from your taxable income.
3. Payments into Pillar 3a
Pillar 3a is still the most effective way to save for retirement tax benefits. In 2025, the annual deductible limit is CHF 7,258 for employees affiliated to a pension fund (up to CHF 36,288 for the self-employed), and these amounts are fully tax-deductible.
4. Setting up an unrestricted pension plan
Once a pension fund purchase has been made, and the maximum payments have been made to Pillar 3A, it is also possible to top up the remaining gaps by taking out a free personal pension plan (3b). A common form of this is traditional or unit-linked life insurance.
Some cantons allow tax deductions for Pillar 3b contributions. This is the case in Geneva, where you can deduct CHF 2,200 per year for a single person. In addition, if the insured person fulfils the conditions of the pension character, the capital will be exempt at the time of payment.
Pension criteria
The purpose of Pillar 3b retirement provision is achieved when:
- Payment is made after age 60
- The contract is taken out before age 66
- Contract duration is 5 years (10 if linked to funds)
5. Private investment
For people with in-depth investment knowledge, investments in actions or ETF via a securities account to increase capital over the long term.
However, the risk of loss is borne alone. And this risk is often considerable, at least in the short to medium term.
How are retirement pensions taxed?
You must declare all your annuities (AHV, BVG and Pillar 3a) as income on your tax return. taxable at 100 %.
Life annuities from unrestricted personal pension plans (3b), on the other hand, are only taxed at 4% with other income.
Every year, your AHV fund and your pension fund automatically send you the following information tax certificates necessary to declare your pensions. You can also request a duplicate of these certificates from your AHV compensation fund or pension fund at any time.
Frequently asked questions
An annuity provides a stable income for life, regardless of your life expectancy or market trends. It is particularly suitable if :
- You're looking for absolute financial security,
- You have a low tolerance for risk,
- You have no experience in asset management,
- You have no other regular retirement income.
Its main drawback: the capital remains in the fund, and no amount is passed on to heirs.
The capital is paid out in a single lump sum, usually at a reduced tax rate (which varies from canton to canton). This choice gives you :
- Total management freedom,
- The opportunity to invest, pay off a mortgage, help your children or optimize your estate,
- A lever for tax optimization, notably by splitting withdrawals.
But be careful: you're responsible for the long-term future of your capital over 25 to 30 years, depending on your life expectancy. This requires rigorous management. In practice, it's very difficult to match the performance offered by the pension fund (conversion rate of 6.8%).
In most cases, a annuity + capital combination offers a good balance: securing a base income with an annuity, while retaining part of the capital for specific needs or projects.
Pillar 3a is the most tax-efficient solution:
Tax-deductible up to CHF 7,258 in 2025 (for employees affiliated to a pension fund),
Available to the self-employed (up to 20% of annual income),
Possibility of investing in funds (equities, bonds, ESG strategies),
Withdrawal permitted up to 5 years before AHV retirement age
Other solutions are possible, notably in 3b (unrestricted pension provision), where tax deductions are available in some cantons and withdrawals are tax-free. Subsequently, you can add to your assets through individual investments in securities, cash, real estate, etc.
To find out whether early retirement is possible, you will need to draw up a balance sheet to analyze projected annuities, assets and liabilities, and identify all sources of income. A budget should also be drawn up to define fixed and variable expenses, as well as the desired standard of living.
Have a pension plan It's a modest investment to avoid costly mistakes.
Redemptions must be carefully planned. Each repurchase is deductible of taxable income, resulting in substantial tax savings, especially for higher incomes.
Buybacks fill the gap contribution gaps (e.g. career breaks, part-time work) and often allow :
-
A better retirement pension,
-
Greater flexibility over the amount of capital that can be withdrawn.
Be careful, however, as you won't be able to make a tax-free capital withdrawal after a buyback. for 3 years.
As soon as possible. At the age of 25, even if retirement seems a long way off, the first few years of working life are a real challenge. crucial to lay the foundations for your pension provision, and early years are ideal for benefiting from the cumulative effect of compound interest (notably via pension funds).
From 40 years oldwe're starting to get better visibility on your professional, family and asset situation. This is the ideal time to carry out an initial, comprehensive pension assessment, identify gaps, plan pension fund purchases, project a retirement age and structure your investments.
From 50 yearsplanning becomes more concrete. You can consider a precise estimate of AHV and BVG pensions, a tax analysis for capital withdrawals (BVG, 3a), asset decumulation strategies, as well as simulating an early or postponed retirement.
Starting early allows you to smooth out your efforts, reduce the financial pressure as you approach retirement, and keep all your options open (early retirement, gradual reduction, flexible retirement, optimized transmission).